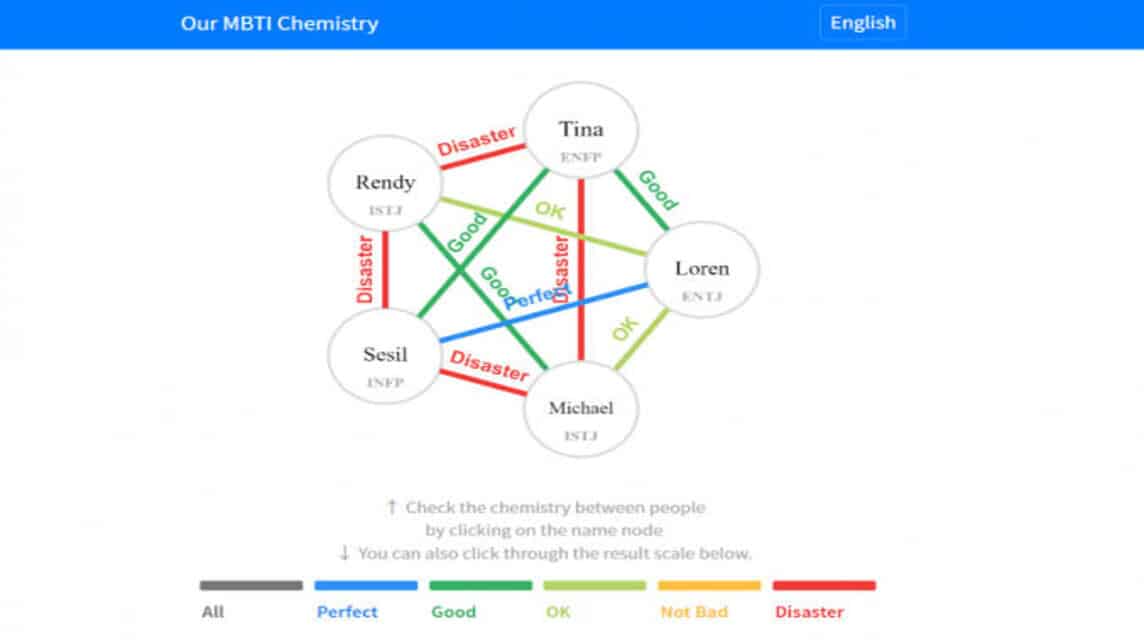
Personality chemistry plays a pivotal role in shaping our interpersonal connections, decision-making processes, and overall life experiences. The Myers-Briggs Type Indicator (MBTI) is one of the most widely recognized frameworks for understanding these dynamics. By delving into the nuances of our personality chemistry through MBTI, we gain invaluable insights into how we interact with others and navigate the world around us.
The MBTI framework categorizes individuals into 16 distinct personality types based on their preferences in four dichotomies: Extraversion (E) vs. Introversion (I), Sensing (S) vs. Intuition (N), Thinking (T) vs. Feeling (F), and Judging (J) vs. Perceiving (P). This system provides a comprehensive lens to explore the complexities of human behavior.
Understanding our personality chemistry through MBTI offers practical benefits in various aspects of life, from enhancing communication and relationships to improving career choices and personal growth. Let's explore the intricacies of this fascinating subject in greater detail.
Read also:Danny Torres Police Officer Unveiling The Story Of A Dedicated Law Enforcement Officer
Table of Contents:
- Biography of MBTI
- History of MBTI
- 16 MBTI Personality Types
- Personality Compatibility
- Communication Styles
- Relationship Dynamics
- MBTI in Career Development
- The Science Behind MBTI
- Criticism and Controversy
- Conclusion
Biography of MBTI
The MBTI framework was developed by Isabel Briggs Myers and her mother, Katharine Cook Briggs, building on the psychological theories of Carl Jung. Their pioneering work began in the early 20th century, aiming to create a practical tool for understanding personality differences.
Key Facts about MBTI Development:
- Initial research started in the 1940s
- Formal publication occurred in 1962
- Ongoing refinements continue to enhance its validity
Data and Biodata
| Founder | Isabel Briggs Myers & Katharine Cook Briggs |
|---|---|
| Year Developed | 1940s |
| First Publication | 1962 |
| Primary Influence | Carl Jung's Psychological Types |
History of MBTI
The origins of MBTI trace back to the groundbreaking work of Swiss psychiatrist Carl Jung, who introduced the concept of psychological types in his seminal book "Psychological Types" in 1921. Myers and Briggs expanded upon these ideas, creating a practical assessment tool that could be applied to everyday life.
Over the decades, MBTI has evolved significantly, with continuous research and development ensuring its relevance in modern contexts. Today, it is used by millions of people worldwide in various settings, including education, business, and personal development.
16 MBTI Personality Types
The MBTI system categorizes individuals into 16 unique personality types, each represented by a four-letter code. These types provide a detailed framework for understanding personality preferences and tendencies.
Read also:Alletta Osean The Rising Star In The World Of Entertainment
Primary Dichotomies
- Extraversion (E) vs. Introversion (I)
- Sensing (S) vs. Intuition (N)
- Thinking (T) vs. Feeling (F)
- Judging (J) vs. Perceiving (P)
Each combination of these preferences results in distinct personality types, such as INTJ (The Architect), ENFP (The Campaigner), and ESFJ (The Consul).
Personality Compatibility
Understanding personality chemistry through MBTI can significantly enhance interpersonal relationships. Compatibility between personality types can be analyzed by examining shared preferences and complementary traits.
For example, individuals with opposite preferences in the Judging-Perceiving dimension may experience challenges in organizing their lives but can learn valuable lessons from each other's approaches.
Key Compatibility Factors
- Shared cognitive functions
- Complementary preferences
- Understanding of differences
Communication Styles
MBTI provides valuable insights into communication preferences, helping individuals adapt their styles to improve interactions. Extraverts tend to think out loud and enjoy verbal communication, while Introverts often prefer written communication and need time to process thoughts.
Sensory types focus on concrete details and practical information, while Intuitive types appreciate abstract concepts and big-picture thinking. Thinkers value logical reasoning, whereas Feelers prioritize emotional intelligence.
Relationship Dynamics
MBTI plays a crucial role in understanding relationship dynamics, whether in romantic partnerships, friendships, or professional collaborations. Recognizing personality differences enables individuals to appreciate each other's strengths and navigate challenges more effectively.
Building Strong Relationships
- Embrace differences as opportunities for growth
- Communicate openly about preferences and needs
- Practice empathy and understanding
MBTI in Career Development
MBTI serves as an invaluable tool in career counseling and personal development. By aligning personality types with suitable career paths, individuals can achieve greater job satisfaction and professional success.
For instance, INTJs often excel in analytical roles such as engineering or strategic planning, while ESFJs thrive in caregiving professions like teaching or healthcare.
Popular Career Paths by MBTI Type
- ENTJ: Leadership roles, management
- ISFJ: Healthcare, social services
- ENFP: Creative fields, counseling
The Science Behind MBTI
The scientific validity of MBTI has been extensively studied, with ongoing research supporting its reliability and validity. While critics question its psychometric properties, proponents highlight its practical applications and widespread acceptance in various fields.
Studies conducted by reputable organizations such as CPP, the official publisher of MBTI, consistently demonstrate its effectiveness in enhancing self-awareness and interpersonal understanding.
Criticism and Controversy
Despite its popularity, MBTI faces criticism regarding its theoretical foundations and statistical validity. Critics argue that its dichotomous nature oversimplifies the complexities of human personality. However, proponents emphasize its value as a starting point for deeper self-exploration and personal growth.
Research published in reputable journals, such as the Journal of Personality Assessment, provides balanced perspectives on MBTI's strengths and limitations.
Conclusion
Our personality chemistry MBTI offers profound insights into human behavior and interpersonal dynamics. By understanding the 16 distinct personality types and their interactions, we can enhance communication, strengthen relationships, and make informed career decisions.
We invite you to explore further resources and share your thoughts in the comments section. Your feedback helps us create more valuable content and foster meaningful discussions about personality development.
Stay connected with our platform for more insightful articles on MBTI and related topics. Together, let's unlock the secrets of personality chemistry and harness its power for personal and professional growth.